Do you own a website or planning to have one?
During or after hosting a website all of you may encounter SSL certificate. But very few of you might know about it. This article will walk you through the SSL guide so that all your doubts can get clear.
As a company owner or an individual, you always make sure that you remain protected from all direct and indirect miss-happenings. SSL certificate acts like online security in the same way you have physical security for your home or business. It protects your website and ultimately your business. In the fast-paced technology world where cybercrime is increasing, one must stay abreast of all these latest advancements. And for this, it is always a wise decision to partner with a reputed SSL provider.
Some hosting companies provide SSL certificate with their hosting plans so, make sure you have it encrypted to your website right from the beginning.
Let’s de-mystify all your questions about SSL certificate.
What is an SSL certificate?
 The SSL stands for “Secure Socket Layer”. It is a technique that establishes a secure connection between the visitor’s web browser and your website. Thus, all the information (communications) that is transmitted through this connection gets encrypted making it secure. SSL is used to transmit confidential emails, files, and other forms of information in a secure way. SSL creates a private and safe channel for you to communicate or send information like private details, banking details, etc.
The SSL stands for “Secure Socket Layer”. It is a technique that establishes a secure connection between the visitor’s web browser and your website. Thus, all the information (communications) that is transmitted through this connection gets encrypted making it secure. SSL is used to transmit confidential emails, files, and other forms of information in a secure way. SSL creates a private and safe channel for you to communicate or send information like private details, banking details, etc.
An SSL certificate is a small piece of code or can also be called a digital computer that has two specific functions :
1) Authentication and Verification :
The SSL certificate contains privilege information or certain details regarding the identity of a person, business or website that will be visible to visitors on your website when they will click on the browser’s padlock symbol or trust mark. The SSL certificate is issued after examining with an Extended Validation (EV) by Certificate Authorities to make it the most trusted SSL certificate available.
2) Data Encryption :
The SSL certificate encrypts confidential information exchanged via the website so that it cannot be accessed or read by anyone other than the intended recipient.
The reliability of SSL certificate increases when it is issued by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA) because CA follows very strict rules and policies about who may and who may not receive an SSL certificate. If you have a valid SSL certificate from trusted CA, then your customers trust you more.
We have seen that SSL certificate encrypts your information, now let’s see how it does so.
How Does SSL Encryption Work?
Encryption uses keys to lock and unlock your information, in the same way, you use a key to lock and unlock doors. Unless you don’t have the right key, you won’t be able to unlock or open the information. That means until the correct encryption key is not used, the information cannot be read.
Each SSL session has two keys :
1) Public Key – This is a key which is used to encrypt or scramble the information.
2) Private Key – This is a key which is used to decrypt or unscramble the information and restore it in its original format so that it can be read.
SSL Encryption Process :
Every SSL certificate that is issued from a verified CA gets issued for a specific server and website domain (website address). When a person uses his browser to access the address of the website incorporated with SSL certificate then an SSL handshake (greeting) occurs between the browser and server. The information is requested from the server and is delivered to the users in their browser window. You will be able to notice changes occurring to indicate that a secure session has been initiated – for example, a green padlock trust mark will appear. If you click on the trust mark you can see some additional information like validity period of SSL certificate, the domain security, type of SSL certificate, and the issuing CA. All this indicate that a secured link is established for that session with a unique session key, and secure communication can begin.
How To Find That a Site Has a Valid SSL Certificate?
1. A standard website without SSL certificate will display “http://” at the beginning of the website address in the browser bar.
The http stands for “Hypertext Transfer Protocol” and is considered as a convenient way to transfer information over the Internet.
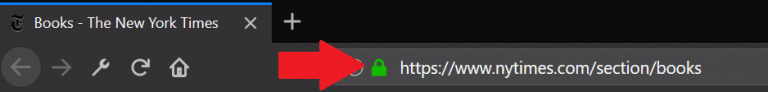
Whereas, a website that is secured with SSL certificate will display “https://” before the address.
The https stands for “Secure HTTP”.
2. You will see a padlock symbol ( as shown in the above image a lock symbol in the address bar).
3. If you click on the padlock in the browser, you can see the authenticated organization name. In the high-security browsers, the authenticated organization name is prominently displayed and the address bar turns green if the Extended Validation (EV) SSL certificate gets detected. If the information does not match or the certificate has already expired, then the browser displays a warning or error message.
4. You can diagnose problems with your SSL certificate installation, by using any of the SSL checker tools.
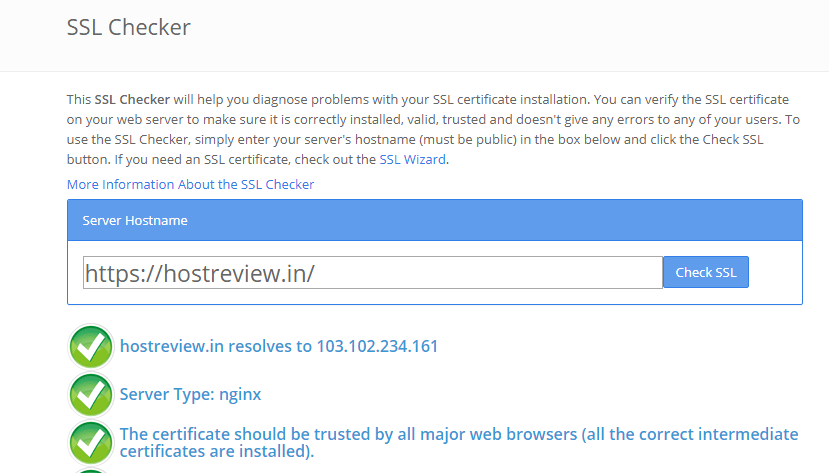
Here you get details like server type, from whom the certificate is issued, certificate’s expiry date, etc.
Where SSL Certificate can be Used?
In simple words, the answer to this question is that you can use SSL certificate anywhere you wish to transfer information securely.
Some of the examples are :
(i) To secure communication between your website and your customer’s internet browser.
(ii) To secure internal communication on your corporate intranet.
(iii) To secure email communication sent to and from your network (or private email address).
(iv) To secure information between servers (both internal and external).
(v) To secure information sent and received via mobile devices.
Related: Importance of SSL certificate for your website
Different Types of SSL Certificates :
There are various types of SSL certificates available in the market today.
1) Self-signed SSL Certificate :
As the name indicates this type of certificate is generated for internal purposes and is not issued by any CA. But, as the website owner generates its own certificate, it does not hold the same weightage as a fully authenticated and verified SSL certificate issued by a CA.
2) Domain Validated Certificates (DV SSL) :
Domain Validation SSL Certificate holds low assurance and basic encryption typically used for blogs and informational websites. This certificate holds very minimal validation process while issuing one. The process only requires website owners to prove their domain ownership by responding to an email or phone call. This is the least expensive and fast process to obtain a certificate. The browser address bar will only display HTTPS and a padlock and won’t include the business name. If you don’t require extra assurance for your website visitors, then you can install a Domain Validation SSL Certificate.
Browser view with DV SSL Certificates
All browsers will only show a green padlock and HTTPS, if DV SSL certificates incorporated :
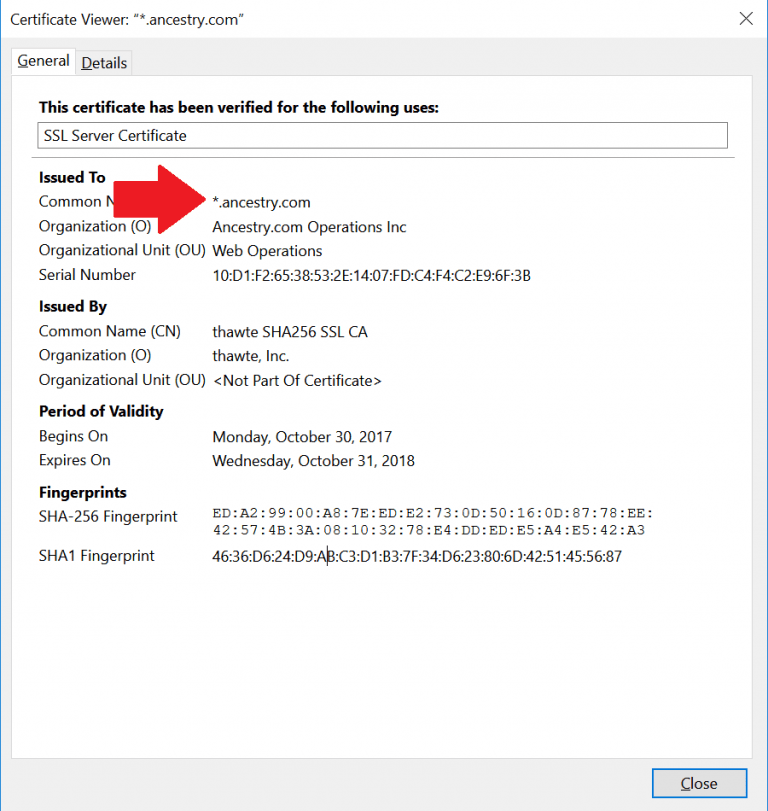
3) Wildcard SSL Certificates :
Wildcard SSL certificates are used to secure a base domain and unlimited sub-domains.
It is cheaper than purchasing several single domain SSL certificates. Wildcard SSL certificates have asterisk * mark as a part of the common name. The asterisk * represents valid sub-domain that has the same base domain. For example, the common name can be *.example.com.
4) Multi-Domain SSL Certificates :
Multi-domain certificates are responsible to secure up to 100 different domain names and sub-domains using a single certificate which can save your time and money. You have control over the Subject Alternative Name (SAN) field to add, change, and delete any of the SANs as needed. Here are some domain name examples that can be secured using one Multi-Domain SSL certificate:
www.domain.com
www.domain.in
www.domain.org
domain.com
checkout.domain.com
mail.domain.com
secure.exampledomain.org
www.website.com
www.example.co.uk
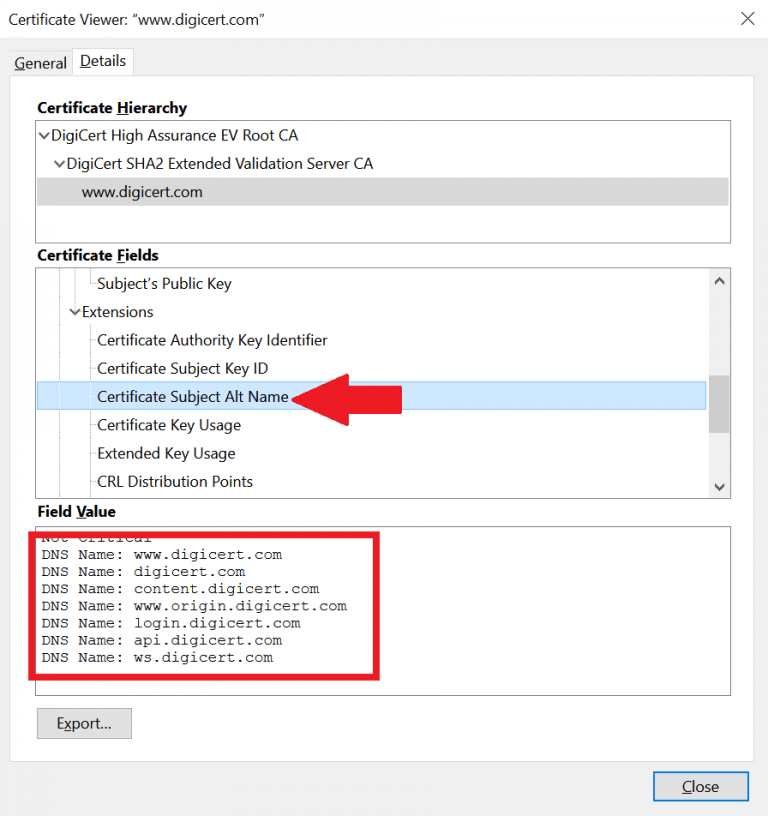
5) Unified Communications Certificates (UCC) :
Unified Communications Certificates (UCC) are also considered as Multi-domain SSL certificates and were originally designed to secure Microsoft Exchange and Live Communications servers. These types of certificates can be used by website owners and also allow multiple domain names to be secured on a single certificate. UCC certificates are organizationally validated and they display a padlock in the browser.
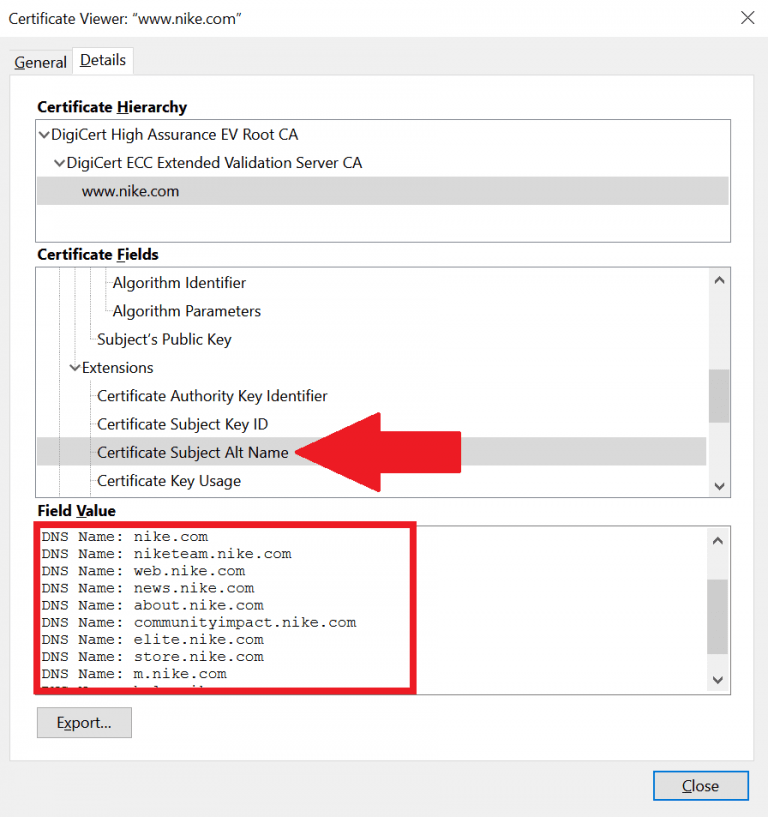
6) Extended Validation Certificates (EV SSL) :
EV SSL is the most expensive and high ranked SSL certificate. When this SSL certificate is installed on your website it will display the padlock, HTTPS, name of the business and the country on the browser address bar. To issue this type of SSL certificate, the website owner will need to go through a standardized identity verification process in order to confirm that the website owner is authorized legally to the exclusive rights of the domain. EV SSL certificates are used in high profile websites containing applications for carrying out the activities related to identity assurance like data collection, process logins or online payments.
Having an SSL certificate incorporated with your site ensures that the website is safe from all hackers and is safe to browse by its visitors. SSL certificate is considered as an important factor in SEO to rank your website higher in search engine results.
SSL Certificate – A Right Choice for your Website
SSL certificate is a must have online security option available for your website. Trust makes a big difference in the online business and incorporating SSL certificate is an effective way to build a trustworthy relationship. Nowadays, many hosting companies provide free SSL certificate with their hosting plans. Thus, once your website gets hosted always check if it is protected with SSL certificate or not.




